
 |
quick manual | algorithms | dx max(4): options, pictures, destroy and repair
Algorithm types
Each of the 6 oscillators (called "operators") consist of only sine waves.
Sine waves can be changed by the modulator. It gives side band frequencies below and above of the carrier.
They interact with each other through 32 different "algorithms".
The 32 algorithms are created using only 12 unique building blocks.
Top-down: red=modulator, blue=carrier (the sound that is modulated).
Feedback: more feedback makes more of a saw of the osc. Too much feedback introduces noise.
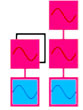 |
Stacked | - 1 or more
modulators
connected
in series to
a single carrier - there can be multiple parallel stacks |
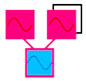 |
Branch | - multiple modulators connected to a single carrier |
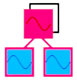 |
Root | - a single modulator connected to multiple carriers to beef up the carrier sounds |
| Carrier-only | - multiple operators in carrier position, no modulators nice for organ sounds |
FM generated waveforms
only 4 parameters we need to change:
- algorithm selection
- operator output level
- feedback level
- coarse frequency
| triangle | 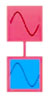 |
- no feedback on modulator needed
|
||||||||||||
| sawtooth | 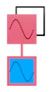 |
- feedback needed
|
||||||||||||
| square |  |
- same as tri and saw
together
|
FM generated filter sweeps
make a sawtooth
go to the envelope generator of the modulator
decay the eg to 0, to decrease the impact of the modulator on the carrier, so the carrier goes to sine
Envelope generators
modulator eg's change the tone over time
carrier eg's change the volume over time
thank you madFame